Design rules
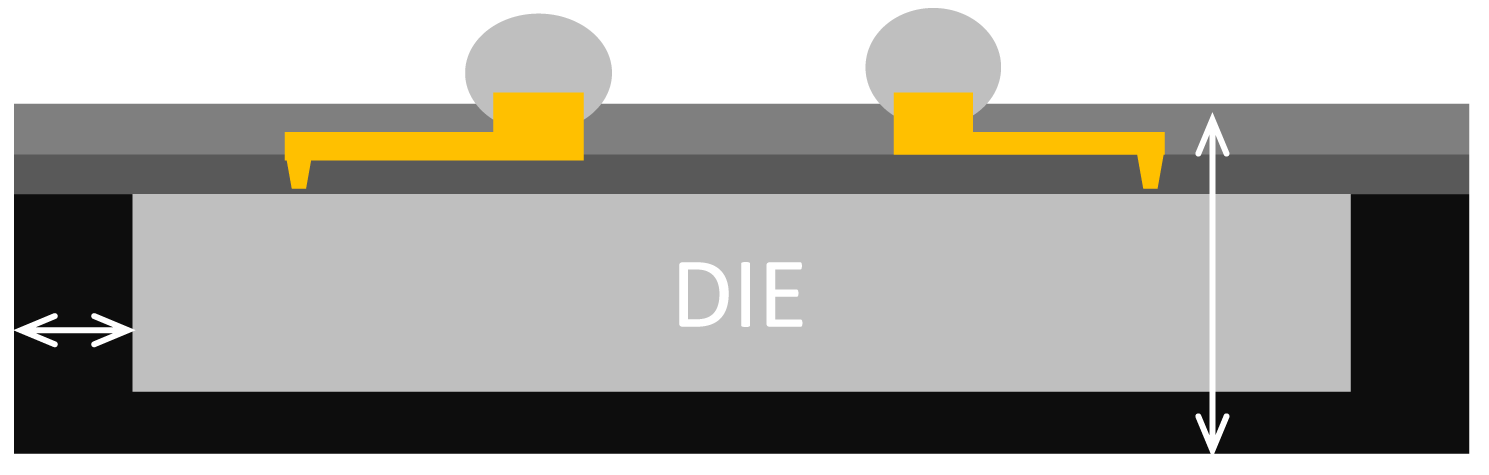
1st Die electric thickness (ABF)
RDL Line – Space
RDL Cu trace thickness *
Stud Cu (Bump) thickness
2nd Die electric thickness (ABF)
Silicon die thickness
Die back mold compound
Pkg thickness
(exclude ball)
EMC side wall thickness
Component Level Reliability Data.
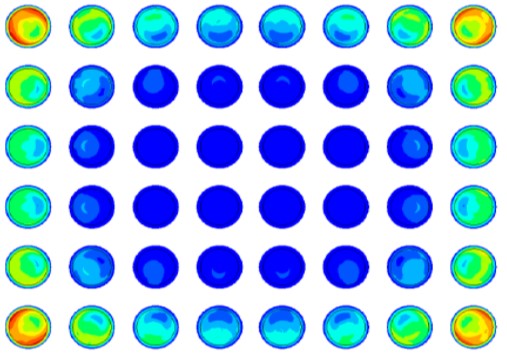
Standard WLCSP
Side and corner bump illustrate a yellowish to reddish colour, highlighting the stress on the corner joints. Over time, the CTE mismatch of the silicon (die) and the PCB create stress in the solder connection. This result in a deterioration of the solder ball reducing the lifespan of the package.
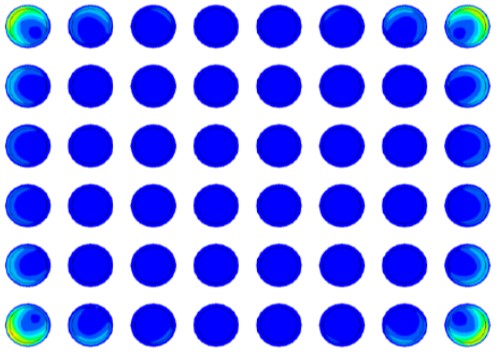
PEP Innovation Protected PLCSP
PEP panel level CSP has a tall copper tower holding the solder ball, creating a stress buffer against elevated current density and electromigration enhancing the lifespan of the package.
Simulation data shows 2 times longer solder life time.
For thermal cycling, the critical joint is at the corner bump, which is the furthest bump location from the neutral point, the package center. The strain energy-density-distribution (SED) for the corner bump at the bump-UBM pad interface can be used to predict the thermal cycle lifetime of the part.
